Breaking New Ground in Brain Visual Decoding: The Revolutionary BASIC Framework
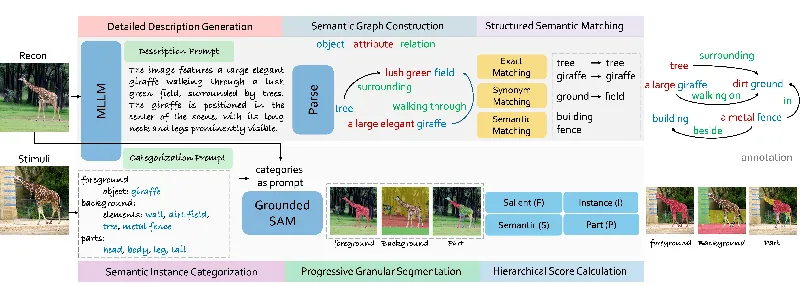
In a groundbreaking study from researchers at Cambridge University, a new framework for assessing brain visual decoding was introduced. This framework, known as BASIC (Brain-Aligned Structural, Inferential, and Contextual similarity), promises to significantly enhance the way we evaluate the accuracy and reliability of models that decode visual information from brain activity.
The Limitations of Current Evaluation Metrics
Historical evaluation methods in the field of brain visual decoding have relied on coarse metrics that often fail to differentiate between the performances of various decoding models. These existing protocols overlook crucial nuances in how human perception processes visual stimuli and lack a strong relation to neuroscientific principles.
The researchers pointed out that conventional metrics either saturate across state-of-the-art models, thereby losing discriminative capacity, or are overly simplistic, failing to account for the complex layers of visual interpretation required by the brain. Consequently, the field has struggled to benchmark its progress effectively, with many differences muddled due to inadequate metrics.
Introducing BASIC: A Multigranular Approach
BASIC seeks to offer a comprehensive evaluation strategy that quantifies how well decoded images capture the structural, inferential, and contextual aspects of true stimuli. By integrating various methods of analysis, it allows for a nuanced evaluation of decoded results across structural fidelity, inferential accuracy, and contextual coherence.
The framework assesses visual decoding from multiple perspectives, including:
- Structural Similarity: Evaluating how reconstructed images align with real-life visual structures.
- Inferential Similarity: Measuring whether the decoded images convey the same conceptual content as the original stimuli.
- Contextual Similarity: Assessing the overall coherence and plausibility of the reconstructed scenes.
A Robust Study Across Diverse Datasets
In their extensive experiments, the researchers benchmarked a variety of visual decoding methods within this unified evaluation framework against multiple datasets—including fMRI and EEG data. The results indicated that their new methodology was able to distinguish model performance more effectively than previous metrics.
One of the highlights from the findings demonstrated that models employing the BASIC framework provided clearer differentiation between object accuracy, semantic alignment, and structural precision, thereby allowing for meaningful diagnostics of where specific decoding methods excelled or failed.
Implications for Future Research
The introduction of BASIC establishes a new standard for evaluating advancements in visual brain decoding, paving the way for more nuanced insights into how we can use AI to interpret brain signals. As the field moves forward, this framework may facilitate the development of more accurate brain-computer interfaces and enhance our understanding of human cognition and perception.
As we strive to better understand the complexities of the human brain, the BASIC framework embodies a significant leap toward ensuring that the methods we employ to decode brain activity are not only scientifically valid but also comprehensive in their evaluation of human visual experiences.